Contact : +91-79045 61980 | Email: hydrofitengineers@gmail.com
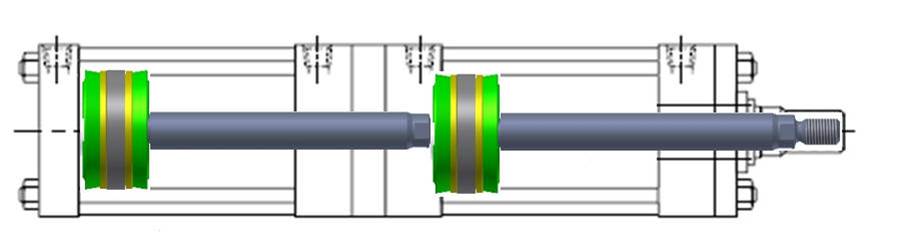


A tandem pneumatic cylinder, also known as a tandem air cylinder or double rod cylinder, is a type of pneumatic actuator that consists of two cylinders connected in series. This design allows for increased force output compared to a single cylinder of the same bore size. Tandem cylinders are commonly used in applications where higher force or pushing and pulling motions are required. Here’s a detailed overview of tandem pneumatic cylinders, including their features, working principles, and applications
Features of Pneumatic Tandem Cylinder
- Increased Force Output:
- The tandem arrangement allows for the combined force output of two cylinders, providing higher force capabilities than a single cylinder of the same bore size.
- Dual Piston Rods:
- Tandem cylinders have two piston rods extending from both ends, offering bidirectional force application and allowing for push and pull motions.
- Compact Design:
- Despite the increased force output, tandem cylinders often maintain a relatively compact design, making them suitable for applications with space constraints.
- Flexible Mounting Options:
- Tandem cylinders typically offer various mounting options, providing flexibility in integration into different systems.
- Bidirectional Control:
- Tandem cylinders can be controlled to extend and retract independently, allowing for precise bidirectional motion.
- Versatility in Applications:
- Due to their increased force capabilities, tandem cylinders find use in applications requiring higher pushing or pulling forces.
Working Principle of Pneumatic Tandem Cylinder
- Extension Stroke:
- Compressed air is introduced into the first cylinder, causing the piston to extend. Simultaneously, compressed air is introduced into the second cylinder, extending its piston as well.
- Retraction Stroke:
- When retracting, compressed air is introduced into the second cylinder, causing its piston to retract. Simultaneously, compressed air is introduced into the first cylinder, retracting its piston.
- Directional Control Valves:
- Directional control valves are used to regulate the flow of compressed air into the different chambers of the tandem cylinder, controlling the direction of motion.
- Independent Control:
- Tandem cylinders can be controlled independently, allowing for precise control over the extension and retraction of each piston.
Applications of Pneumatic Tandem Cylinder
- Pressing and Forming:
- Tandem cylinders are commonly used in applications where higher force is needed for pressing, forming, or stamping operations.
- Material Handling:
- Conveyor systems and material handling equipment benefit from the increased force output of tandem cylinders for lifting and pushing loads.
- Automation and Robotics:
- Tandem cylinders are integrated into robotic systems for tasks that require higher force capabilities, such as heavy part manipulation.
- Clamping and Gripping:
- Applications involving clamping and gripping benefit from the increased force provided by tandem cylinders.
- Injection Molding Machines:
- Tandem cylinders are used in injection molding machines for precise control over the movement of the molding components.
- Metal Forming Machinery:
- Hydraulic presses and metal forming machinery often use tandem cylinders for shaping and pressing operations.
Considerations and Maintenace of Pneumatic Tandem Cylinders
- Seal Integrity:
- Regular inspection of seals is essential to prevent air leaks and ensure efficient operation.
- Alignment:
- Proper alignment of the tandem cylinders is crucial to ensure uniform force distribution.
- Air Quality:
- Clean and dry compressed air is necessary to prevent damage to seals and ensure reliable performance.
- Lubrication:
- Lubrication of moving parts, including piston rods and seals, is important for smooth operation and prevention of wear.
Tandem pneumatic cylinders are valuable components in various industrial applications where increased force output is required. Their bidirectional force application, compact design, and versatility make them suitable for a wide range of tasks in manufacturing, automation, and material handling. Regular maintenance and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of tandem cylinders in their intended applications.
