Contact : +91-79045 61980 | Email: hydrofitengineers@gmail.com
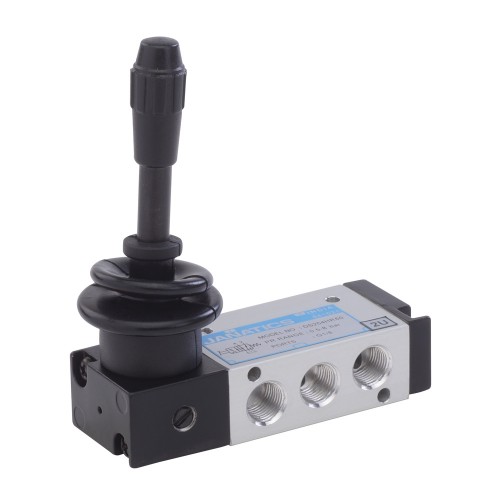



Hand operated pneumatic valve are devices used to control the direction of airflow in a pneumatic system manually. These valves play a crucial role in regulating the movement of pneumatic actuators, such as cylinders and rotary actuators
Types of Hand Operated Pneumatic Valve for Direction Control
Manual Direction Control Valves
These valves use a lever that can be manually shifted to different positions to control the airflow direction
Hand lever operated pneumatic valves for direction control of compressed air are manually actuated devices used to control the flow of compressed air within a pneumatic system. These valves are essential for directing air to different parts of the system, enabling the control of pneumatic actuators, cylinders, and other components. Here’s an overview of their key features and functions:
Key Features
- Manual Operation: These valves are operated by hand using a lever, which makes them simple to use and allows for quick manual control of pneumatic systems.
- Directional Control: They can direct the airflow in different directions, typically in 2-way, 3-way, or 4-way configurations.
- Versatility: Suitable for various industrial applications where manual control is preferred or required.
- Robust Construction: Often made from durable materials to withstand harsh industrial environments.
- Locking Mechanisms: Some models may include a locking feature to maintain the valve in a specific position.
Common Types
- 2-Way Valves: These have two ports and control the flow of air from one port to the other.
- 3-Way Valves: These have three ports and can direct airflow between two outputs or control a single output with an exhaust port.
- 4-Way Valves: These have four ports and are used to control double-acting cylinders by directing air to either side of the cylinder.
Applications
- Machinery Control: Used in various machines for controlling pneumatic cylinders and actuators.
- Automation Systems: Integral parts of automated systems where manual override or control is necessary.
- Industrial Equipment: Found in factories and workshops to control tools and machinery powered by compressed air.
Operation
To operate a hand lever pneumatic valve, the user moves the lever to different positions. Each position corresponds to a specific configuration of the internal ports, directing the airflow as required by the system’s design.
These valves are critical for ensuring precise control and flexibility in pneumatic systems, especially in settings where manual intervention is necessary or preferred.
Hand Wheel Direction Control Valves
In this type of Hand Operated Pneumatic Valve, hand wheels are rotated to control the valve and, consequently, the direction of the airflow
Hand wheel operated pneumatic direction control valves are manually actuated valves that use a hand wheel for operation. These valves control the direction of airflow in a pneumatic system, and they are designed for applications where precise manual control is needed. Here’s an overview of their features, types, and applications:
Key Features
- Manual Operation: Operated by a hand wheel, allowing for fine and precise control of the valve position and airflow direction.
- Directional Control: Can direct the airflow to different parts of the pneumatic system, typically in 2-way, 3-way, or 4-way configurations.
- Durable Construction: Made from robust materials to withstand industrial environments.
- Precision: The hand wheel allows for gradual adjustments, providing precise control over the airflow.
- Locking Mechanisms: Some models may include a locking feature to hold the valve in a specific position.
Common Types
- 2-Way Valves: These have two ports and control the flow of air from one port to the other, suitable for simple on/off control.
- 3-Way Valves: These have three ports and can direct airflow between two outputs or control a single output with an exhaust port, suitable for controlling single-acting cylinders.
- 4-Way Valves: These have four ports and are used to control double-acting cylinders by directing air to either side of the cylinder, allowing for forward and reverse motion.
Applications
- Machinery Control: Used in various machines to manually control pneumatic cylinders and actuators.
- Automation Systems: Integral parts of automated systems where precise manual control is required.
- Industrial Equipment: Commonly found in factories and workshops to control tools and machinery powered by compressed air.
- Maintenance and Testing: Ideal for maintenance tasks and testing pneumatic systems due to their precise control capabilities.
Operation
To operate this type of hand operated pneumatic valve, the user turns the hand wheel to different positions. Each position corresponds to a specific configuration of the internal ports, directing the airflow as needed by the system. The hand wheel allows for gradual and precise adjustments, making these valves suitable for applications requiring fine control.
Hand wheel operated pneumatic valves are essential for applications where precise and reliable manual control of pneumatic systems is crucial. They provide the flexibility and accuracy needed to ensure optimal performance and safety in various industrial settingsIn th.
Palm Button Direction Control Valves
These valves have a palm or push-button that, when pressed, actuates the valve to change the airflow direction
Palm button pneumatic direction control valves are manually operated valves that use a large button (palm button) for actuation. These valves are designed for applications requiring easy and quick manual control of the airflow in a pneumatic system. Here’s an overview of their features, types, and applications:
Key Features
- Manual Operation: Activated by pressing a large, easily accessible button, making it simple to operate even with gloved hands.
- Directional Control: Controls the direction of airflow within the pneumatic system, available in various configurations such as 2-way, 3-way, and 4-way.
- Ergonomic Design: The palm button is designed for ease of use, providing a comfortable and efficient means of control.
- Durable Construction: Built to withstand industrial environments, often made from robust materials.
- Quick Actuation: Allows for rapid engagement and disengagement of the valve, suitable for applications requiring fast response times.
Common Types
- 2-Way Valves: These have two ports and control the flow of air from one port to the other, suitable for simple on/off control.
- 3-Way Valves: These have three ports and can direct airflow between two outputs or control a single output with an exhaust port, commonly used for controlling single-acting cylinders.
- 4-Way Valves: These have four ports and are used to control double-acting cylinders by directing air to either side of the cylinder, allowing for forward and reverse motion.
Applications
- Machinery Control: Used in various machines to manually control pneumatic cylinders and actuators.
- Safety Systems: Integrated into safety systems for emergency stop functions or quick manual overrides.
- Industrial Equipment: Found in factories and workshops to control tools and machinery powered by compressed air.
- Maintenance and Testing: Ideal for maintenance tasks and testing pneumatic systems due to their ease of use and quick actuation.
Operation
To operate a palm button pneumatic valve, the user presses the large button. This action changes the configuration of the internal ports, directing the airflow as required by the system. The palm button design allows for quick and easy operation, making these valves suitable for applications where fast manual control is needed.
Advantages
- Ease of Use: The large button is easy to press, even with gloves, reducing operator fatigue.
- Quick Response: The valve can be quickly engaged or disengaged, providing immediate control over the pneumatic system.
- Safety: The palm button can be used in emergency stop applications, providing a reliable means of quickly shutting down pneumatic equipment.
Palm button pneumatic direction control valves are essential in applications requiring straightforward and rapid manual control. Their ergonomic design and quick actuation make them suitable for a wide range of industrial and safety applications.
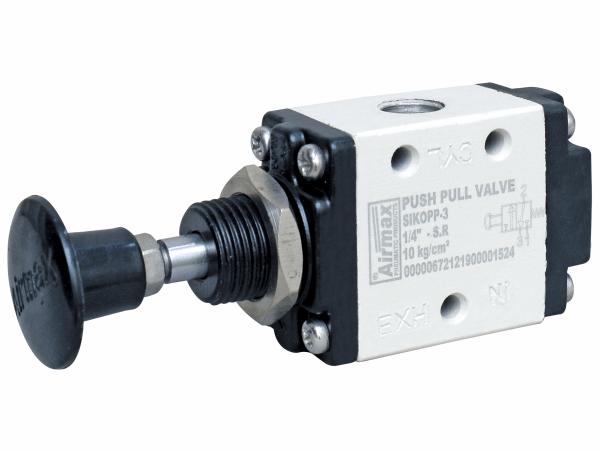
Push Pull Direction Control Valves
Valves with a push-pull mechanism where pushing or pulling the control element changes the valve state
Push-pull pneumatic direction control valves are manually operated valves that use a push-pull mechanism for actuation. These valves control the direction of airflow in a pneumatic system and are designed for applications where a straightforward and robust manual operation is required. Here’s an overview of their features, types, and applications:
Key Features
- Manual Operation: Operated by pushing or pulling a knob or handle, providing a simple and intuitive control method.
- Directional Control: Directs the airflow in different directions, typically in 2-way, 3-way, or 4-way configurations.
- Durable Construction: Built from robust materials to withstand industrial environments.
- Quick Actuation: Allows for fast switching between valve positions, suitable for applications requiring immediate response.
- Positive Feedback: The push-pull mechanism provides clear tactile feedback, ensuring the operator knows the valve’s position.
Common Types
- 2-Way Valves: These have two ports and control the flow of air from one port to the other, suitable for simple on/off control.
- 3-Way Valves: These have three ports and can direct airflow between two outputs or control a single output with an exhaust port, typically used for controlling single-acting cylinders.
- 4-Way Valves: These have four ports and are used to control double-acting cylinders by directing air to either side of the cylinder, allowing for forward and reverse motion.
Applications
- Machinery Control: Used in various machines to manually control pneumatic cylinders and actuators.
- Industrial Equipment: Commonly found in factories and workshops to control tools and machinery powered by compressed air.
- Maintenance and Testing: Ideal for maintenance tasks and testing pneumatic systems due to their simple operation.
- Mobile Equipment: Often used in mobile pneumatic equipment where a rugged and reliable manual control is needed.
Operation
To operate a push-pull pneumatic valve, the user pushes or pulls the handle or knob. This action changes the configuration of the internal ports, directing the airflow as required by the system. The push-pull mechanism provides quick and decisive control, making these valves suitable for applications where rapid and straightforward manual operation is essential.
Advantages
- Simplicity: The push-pull operation is easy to understand and use, minimizing training requirements for operators.
- Speed: Allows for fast actuation, providing immediate control over the pneumatic system.
- Reliability: The robust construction and positive feedback ensure reliable operation even in harsh conditions.
- Safety: The clear tactile feedback helps prevent accidental valve position changes, enhancing operational safety.
Push-pull pneumatic direction control valves are essential in applications requiring simple, fast, and reliable manual control. Their straightforward operation and durable design make them suitable for a wide range of industrial and mobile applications.
Rotary Direction Control Hand Valves
Rotation of a hand-operated knob or wheel changes the position of internal components, directing the airflow
Pneumatic rotary direction control valves are a type of valve that uses a rotary motion to control the direction of airflow in a pneumatic system. These valves are designed for applications where precise and smooth control is needed. Here’s an overview of their features, types, and applications:
Key Features
- Rotary Motion: Operated by rotating a handle, knob, or lever, providing smooth and controlled actuation.
- Directional Control: Directs the airflow in different directions, typically in 2-way, 3-way, or 4-way configurations.
- Durable Construction: Built from robust materials to withstand industrial environments.
- Precision Control: Allows for fine adjustments, making it suitable for applications requiring precise control.
- Locking Mechanisms: Some models may include a locking feature to maintain the valve in a specific position.
Common Types
- 2-Way Valves: These have two ports and control the flow of air from one port to the other, suitable for simple on/off control.
- 3-Way Valves: These have three ports and can direct airflow between two outputs or control a single output with an exhaust port, commonly used for controlling single-acting cylinders.
- 4-Way Valves: These have four ports and are used to control double-acting cylinders by directing air to either side of the cylinder, allowing for forward and reverse motion.
Applications
- Machinery Control: Used in various machines to manually control pneumatic cylinders and actuators.
- Automation Systems: Integral parts of automated systems where precise manual control is required.
- Industrial Equipment: Commonly found in factories and workshops to control tools and machinery powered by compressed air.
- Flow Regulation: Ideal for applications requiring precise control over airflow, such as in fluid handling systems and process control.
Operation
To operate a pneumatic rotary direction control valve, the user rotates the handle, knob, or lever to different positions. Each position corresponds to a specific configuration of the internal ports, directing the airflow as required by the system. The rotary motion allows for fine and precise adjustments, making these valves suitable for applications where smooth and accurate control is needed.
Advantages
- Smooth Operation: The rotary motion provides a smooth and continuous control action, reducing wear and tear on the valve components.
- Precision: Allows for precise adjustments, making it ideal for applications requiring accurate control of airflow.
- Durability: The robust construction ensures long-lasting performance even in harsh industrial environments.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications, from simple on/off control to complex flow regulation tasks.
Pneumatic rotary direction control valves are essential in applications requiring smooth, precise, and reliable manual control. Their rotary actuation mechanism provides an intuitive and efficient means of controlling the direction and flow of compressed air in various industrial and automation settings.
Functions of Hand operated Pneumatic Valve
Direction Control
- The primary function is to control the direction of airflow in a pneumatic system, determining the movement of pneumatic actuators.
Manual Operation
- These valves are manually operated by an operator, allowing for precise control over the pneumatic system.
Design of Hand operated Pneumatic Valve
Body Material
Typically made of materials like aluminum, stainless steel, or other corrosion-resistant alloys to withstand pneumatic system conditions
Control Element
The hand-operated control element, whether a lever, wheel, button, or knob, is designed for ergonomic and easy manual operation
Internal Mechanism
The internal mechanism includes seals, springs, and other components to ensure a reliable and leak-free operation
Working Principle of Hand operated Pneumatic Valve
Positional Control
The valve has multiple positions, and manually changing the position of the control element shifts internal components, determining the pathway of compressed air
Pneumatic Actuation
The valve controls the actuation of pneumatic devices by directing compressed air to different ports based on the chosen position
Two Position or Three Position Valves
Some valves have two positions (on/off) or three positions (center/off-center), providing different flow paths
Spring Return
Some hand operated valves are spring-loaded, returning to a default position when the operator releases the control element
Hand operated pneumatic valves are essential components in pneumatic systems, allowing operators to manually control the direction of airflow and consequently regulate the movement of pneumatic actuators. The design and type of valve depend on the specific requirements of the application
