Contact : +91-79045 61980 | Email: hydrofitengineers@gmail.com
Weld Neck Flange
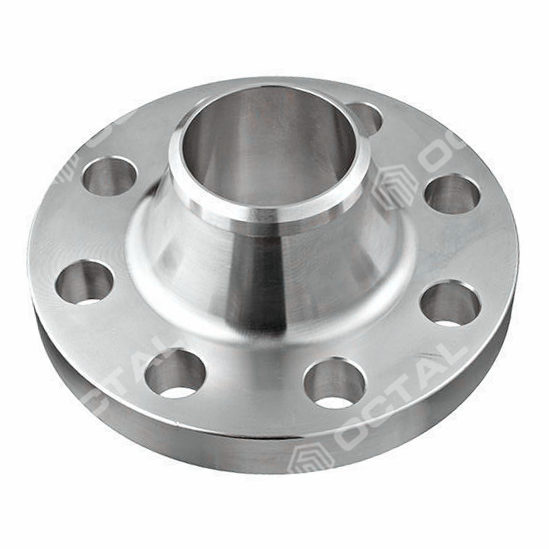

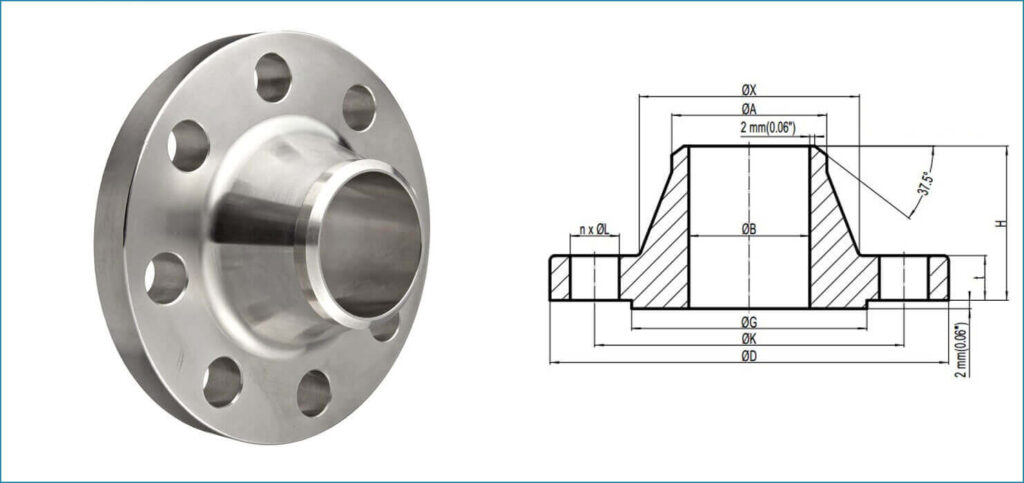
A weld neck flange is a type of flange designed to be welded to the end of a pipe, providing a robust and stable connection. Here are key features and characteristics of weld neck flanges
Key Features of Weld Neck Flange
- Neck Design:
- Weld neck flanges have a long, tapered neck that extends from the flange base to the pipe.
- The extended neck provides additional reinforcement to the connection.
- Welding Hub:
- The neck is welded to the pipe, creating a strong and permanent joint.
- The welding hub distributes the stress from the flange to the pipe, reducing stress concentration.
- Bore Size:
- The bore size of a weld neck flange matches the inside diameter of the connected pipe.
- This ensures a smooth flow of fluids or gases through the piping system.
- Raised Face or Ring Type Joint:
- Weld neck flanges may have a raised face or a groove for a ring-type joint (RTJ) gasket, depending on the application and sealing requirements.
- Pressure Rating:
- Available in various pressure ratings, making them suitable for a wide range of applications from low to high pressures.
- Material Compatibility:
- Weld neck flanges are available in different materials, with stainless steel being a common choice due to its corrosion resistance.
7. Applications:
- Weld neck flanges are widely used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications, such as in the oil and gas industry, petrochemical plants, and power generation facilities.
- Commonly used in pipelines and systems requiring a strong and reliable connection.
Advantages of Weld Neck Flange
- Strength and Reinforcement:
- The extended neck provides structural reinforcement, making weld neck flanges suitable for applications with high pressure and temperature.
- Reduced Stress Concentration:
- The gradual transition from the flange to the neck reduces stress concentration, improving the overall strength of the connection.
- Ideal for High-Stress Situations:
- Well-suited for applications where the pipe is subjected to bending, torsional loads, or thermal expansion.
- Smooth Flow:
- The continuous and smooth transition from the flange to the pipe bore minimizes turbulence and pressure drop in the piping system.
- Sealing Options:
- Weld neck flanges can accommodate various types of gaskets, including flat gaskets for raised face flanges and ring-type joint (RTJ) gaskets for grooved flanges.
Points to consider when selecting a Weld Neck Flange
- More Complex Installation:
- The welding process involved in attaching the flange to the pipe requires skilled labor and careful welding practices.
- Cost:
- Weld neck flanges may be more expensive compared to some other types of flanges due to their design and welding requirements.
Weld neck flanges are chosen for applications where the combination of strength, durability, and resistance to high pressures and temperatures is crucial. Proper welding procedures and adherence to industry standards are essential for ensuring the integrity of the weld joint in weld neck flange applications
General Sizes of Weld Neck Flanges
Weld neck flanges are available in a wide range of sizes to accommodate various pipe diameters and applications. The sizing of weld neck flanges is typically specified by the nominal pipe size (NPS) or nominal bore size, which corresponds to the inside diameter of the connected pipe. Here are some common sizes of weld neck flanges and their corresponding nominal pipe sizes:
- 1/2″ Weld Neck Flange:
- Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): 1/2 inch
- Commonly used in smaller piping systems.
- 3/4″ Weld Neck Flange:
- Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): 3/4 inch
- Suitable for smaller pipes and applications with lower flow rates.
- 1″ Weld Neck Flange:
- Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): 1 inch
- Common size for a variety of applications.
- 1 1/2″ Weld Neck Flange:
- Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): 1 1/2 inch
- Used in larger piping systems and applications requiring increased flow capacity.
- 2″ Weld Neck Flange:
- Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): 2 inches
- A standard size used in various industrial applications.
- 3″ Weld Neck Flange:
- Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): 3 inches
- Suitable for larger pipes and applications with higher flow rates.
- 4″ Weld Neck Flange:
- Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): 4 inches
- Common size for industrial and commercial piping systems.
- 6″ Weld Neck Flange:
- Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): 6 inches
- Used in larger piping systems and applications requiring substantial flow capacity.
- 8″ Weld Neck Flange:
- Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): 8 inches
- Commonly used in industrial settings for larger pipes.
- 10″ Weld Neck Flange:
- Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): 10 inches
- Suitable for larger pipes and heavy-duty applications.
- 12″ Weld Neck Flange:
- Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): 12 inches
- Used in large-scale industrial applications.
These sizes are just examples, and weld neck flanges are available in a wide range of sizes beyond those listed here. The selection of the appropriate size depends on the specific requirements of the piping system, including the diameter of the connected pipes, pressure rating, and flow characteristics. It’s essential to follow industry standards and specifications when selecting weld neck flanges to ensure compatibility with the piping system components.
