Contact : +91-79045 61980 | Email: hydrofitengineers@gmail.com
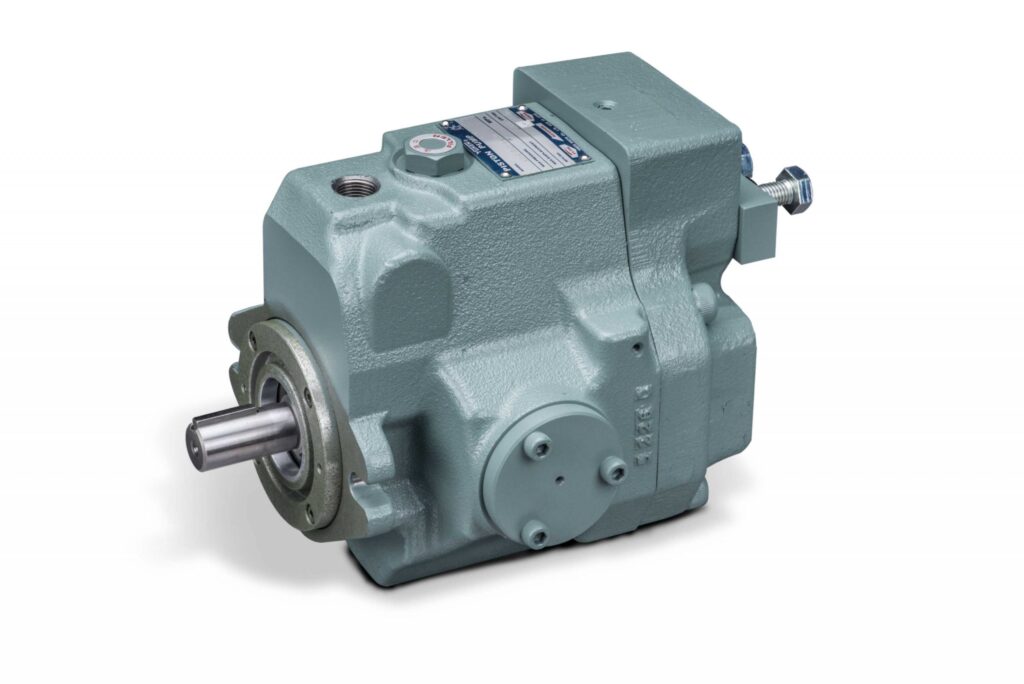
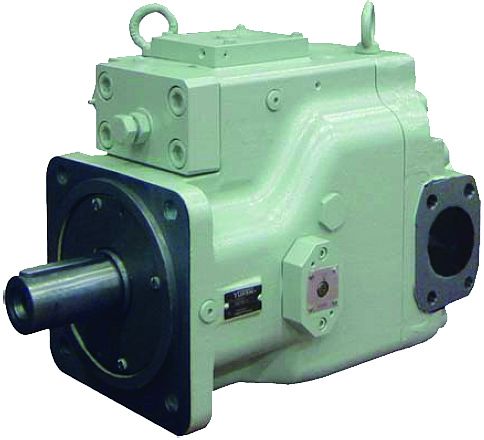
Hydraulic Axial Piston Pumps
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
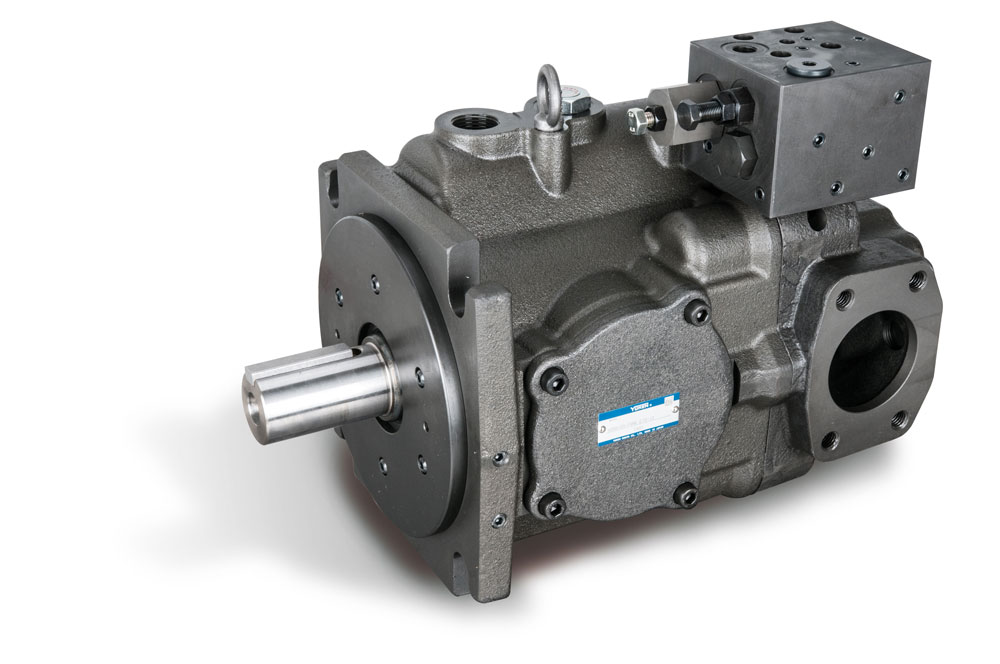
A3H Series Variable Displacement Piston Pumps from Yuken
Hydraulic axial piston pumps are a type of positive displacement pump commonly used in hydraulic systems to generate fluid flow. They work by converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy which is then used to power various hydraulic components such as hydraulic motors, cylinders, and valves
Operation of Axial Piston Pump
- Axial Piston Design: These pumps consist of a series of pistons arranged in a circular pattern within a cylinder block. The pistons move parallel to the axis of rotation of the cylinder block.
- Rotation: The cylinder block rotates around its axis within a stationary housing. As the cylinder block rotates, the pistons reciprocate back and forth within their respective cylinder bores.
- Suction and Discharge: During rotation, the pistons go through an intake stroke where they draw hydraulic fluid (usually oil) into the cylinder bore through an inlet port. Then, as the cylinder block continues to rotate, the pistons undergo a compression stroke where they push the fluid out of the cylinder bore through a discharge port.
- Output Flow: The combined output from all the pistons creates a continuous flow of hydraulic fluid. The flow rate can be adjusted by controlling the speed of rotation or the displacement of the pistons.
- Pressure: The pressure generated by hydraulic axial piston pumps depends on factors such as the force exerted by the pistons, the resistance offered by the load, and the system’s design. Higher pressure can be achieved by increasing the force exerted by each piston or by increasing the speed of rotation.
Working Principle of Hydraulic Piston Pump
The working principle of axial piston pumps revolves around the conversion of mechanical energy into hydraulic energy through the reciprocating motion of pistons within a cylinder block.
Construction of Pump
Axial piston pumps typically consist of a cylinder block, pistons, a swash plate mechanism, a drive shaft, and inlet/outlet ports. The cylinder block houses a series of pistons arranged in a circular pattern around a drive shaft. The swash plate is connected to the drive shaft and can be tilted to control the displacement of the pistons
Intake Stroke
As the drive shaft rotates, the swash plate mechanism causes the pistons to move back and forth within their respective cylinder bores. During the intake stroke, as a piston moves away from the center of the cylinder block, it creates a partial vacuum in the cylinder bore, causing hydraulic fluid (usually oil) to be drawn in through an inlet port
Compression Stroke
As the cylinder block continues to rotate, the swash plate mechanism tilts, causing the pistons to move towards the center of the cylinder block. During the compression stroke, each piston compresses the fluid in its cylinder bore, forcing it out through an outlet port
Continuous Flow
The combined action of all the pistons creates a continuous flow of hydraulic fluid from the inlet port to the outlet port. The flow rate is determined by factors such as the displacement of the pistons, the speed of rotation, and the angle of the swash plate
Pressure Regulation
The pressure generated by the axial piston pump depends on factors such as the force exerted by the pistons, the resistance offered by the load, and the design of the pump. Pressure regulation can be achieved by adjusting the angle of the swash plate, controlling the speed of rotation, or using additional pressure control valves in the hydraulic system
Efficiency and Reliability
Axial piston pumps are known for their efficiency, reliability, and ability to generate high pressure. They are widely used in various applications where precise control of fluid flow and pressure is required, such as industrial machinery, construction equipment, and automotive systems
Overall, axial piston pumps offer a versatile and efficient solution for hydraulic power transmission in a wide range of applications
Design of Hydraulic Axial Piston Pump
Cylinder Block
The core component of an axial piston pump is the cylinder block, which contains a series of cylindrical bores arranged radially around a central shaft. Each bore houses a piston.
Pistons
Pistons are positioned within the bores of the cylinder block. They are typically arranged in a circular pattern and connected to the central shaft via a swash plate or a slipper pad. Pistons move in and out of the bores during operation
Swash Plate or Slipper Pad
This mechanism converts the rotational motion of the drive shaft into reciprocating motion of the pistons. It can be tilted to control the displacement of the pistons, thereby regulating the flow rate of hydraulic fluid
Drive Shaft
The drive shaft is connected to a power source, such as an electric motor or an engine. It provides the rotational motion necessary to drive the pump
Inlet and Outlet Ports
Hydraulic fluid enters the pump through an inlet port and exits through an outlet port. The ports are typically located on opposite sides of the cylinder block
Function of Hydraulic Axial Piston Pump
Intake Stroke
As the drive shaft rotates, the swash plate or slipper pad mechanism causes the pistons to move outward from the center of the cylinder block. This creates a partial vacuum in the cylinder bores, drawing hydraulic fluid into the pump through the inlet port.
Compression Stroke
As the cylinder block continues to rotate, the swash plate or slipper pad mechanism tilts in the opposite direction, causing the pistons to move inward towards the center of the cylinder block. This compresses the hydraulic fluid within the cylinder bores, forcing it out through the outlet port
Flow Control
The displacement of the pistons and the angle of the swash plate or slipper pad mechanism determine the flow rate of hydraulic fluid through the pump. By adjusting these parameters, the pump can deliver varying flow rates to meet the requirements of the hydraulic system
Pressure Regulation
The pressure generated by the pump depends on factors such as the force exerted by the pistons, the resistance of the hydraulic system, and the pump’s design. Higher pressures can be achieved by increasing the force exerted by the pistons or by adjusting the pump’s displacement.
Advantages Of Axial Piston Pumps
Axial piston pumps offer several advantages that make them popular choices in hydraulic systems across various industries
High Efficiency
Axial piston pumps are known for their high efficiency, often exceeding 90%. This efficiency is achieved through precision engineering, low internal leakage, and minimal energy loss during operation. High efficiency translates to lower energy consumption, reduced operating costs, and improved overall system performance
High Pressure Capability
Axial piston pumps are capable of generating high hydraulic pressures, making them suitable for applications that require high-pressure fluid delivery. They can deliver pressures ranging from hundreds to thousands of bar (or psi), depending on the pump design and configuration. High-pressure capability allows axial piston pumps to power demanding hydraulic systems, such as heavy-duty machinery and hydraulic presses
Variable Displacement
Many axial piston pumps feature variable displacement, meaning they can adjust the volume of fluid delivered per rotation of the pump shaft. This feature allows precise control over flow rate and pressure, making axial piston pumps suitable for applications where variable output is required, such as in hydraulic drives and control systems
Compact and Light Weight
Axial piston pumps are often more compact and lightweight compared to other types of hydraulic pumps with similar performance capabilities. Their compact size and relatively low weight make them suitable for integration into space-constrained or weight-sensitive applications, such as mobile equipment, aircraft, and automotive systems
Smooth Operation
The design of axial piston pumps often results in smooth and quiet operation. This characteristic is particularly important in applications where noise and vibration need to be minimized, such as in precision machinery, medical equipment, and passenger vehicles.
Long Service Life
Axial piston pumps are typically built with high-quality materials and precision manufacturing processes, ensuring durability and long service life even under demanding operating conditions. Proper maintenance and regular servicing can further extend the lifespan of axial piston pumps, reducing downtime and maintenance costs
Versatility
Axial piston pumps are versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications across various industries, including manufacturing, construction, agriculture, aerospace, marine, and automotive. Their flexibility, combined with their performance and efficiency characteristics, makes them a preferred choice for many hydraulic system designers and operators
Applications of Axial Piston Pumps
Axial piston pumps find extensive applications across a wide range of industries due to their efficiency, high-pressure capabilities, and precise control over flow rates
Industrial Machinery
Axial piston pumps are used in various industrial applications, including machine tools, metalworking equipment, injection molding machines, and industrial presses. They provide the hydraulic power required for clamping, lifting, pressing, and other manufacturing processes
Construction Equipment
Hydraulic systems in construction machinery such as excavators, loaders, cranes, and bulldozers rely on axial piston pumps for functions like lifting, tilting, steering, and propulsion. Their ability to generate high pressures makes them well-suited for heavy-duty tasks in construction sites
Agricultural Machinery
Axial piston pumps power hydraulic systems in agricultural equipment like tractors, harvesters, sprayers, and irrigation systems. They enable functions such as steering, lifting, lowering, and controlling the movement of implements, enhancing productivity and efficiency in farming operations
Material Handling Equipment
Forklifts, pallet jacks, conveyors, and other material handling equipment utilize axial piston pumps to operate hydraulic cylinders and motors for lifting, tilting, pushing, and pulling loads. Their precise control over flow rates and pressures ensures smooth and accurate handling of materials
Automotive Systems
In automotive applications, axial piston pumps are used in power steering systems to provide the hydraulic assistance needed for steering control. They are also found in hydraulic brake systems and suspension systems, contributing to vehicle safety, comfort, and performance
Aviation and Aerospace
Aircraft and aerospace systems utilize axial piston pumps for various functions, including landing gear actuation, flight control surfaces, hydraulic brakes, and thrust reversers. Their compact size, high-pressure capabilities, and reliability make them suitable for use in aircraft hydraulic systems
Marine and Offshore applications
Axial piston pumps are employed in marine vessels, offshore platforms, and subsea equipment for tasks such as cargo handling, steering, winching, and stabilizing. Their robust construction and resistance to harsh marine environments make them well-suited for marine applications
Renewable Energy
Hydraulic systems in renewable energy applications, such as wind turbines and solar tracking systems, utilize axial piston pumps for adjusting the pitch of turbine blades and tracking the movement of solar panels. Their efficiency and precise control contribute to optimizing energy production
Oil and Gas
Axial piston pumps play a vital role in oil and gas exploration, production, and refining processes. They are used in drilling rigs, wellhead control systems, hydraulic fracturing equipment, and pipeline operations for various hydraulic functions
Power Generation
Power plants and utilities employ axial piston pumps in steam turbines, hydroelectric generators, and other power generation equipment for tasks such as controlling valve actuators, regulating flow rates, and operating hydraulic systems
Add Your Heading Text Here
High Pressure Valves are a range of Heavy Duty robustly constructed Bar Stock for Forged Body Valves which are used for Hydraulic or Instrumentation Lines for Challenging applications
Add Your Heading Text Here
High Pressure Valves are a range of Heavy Duty robustly constructed Bar Stock for Forged Body Valves which are used for Hydraulic or Instrumentation Lines for Challenging applications
Add Your Heading Text Here
High Pressure Valves are a range of Heavy Duty robustly constructed Bar Stock for Forged Body Valves which are used for Hydraulic or Instrumentation Lines for Challenging applications