Contact : +91-79045 61980 | Email: hydrofitengineers@gmail.com
Hydraulic Proportional Valve
Precision Flow & Pressure Control Solutions
These hydraulic proportional valves are designed to provide accurate and precise control of flow and pressure in the latest advanced hydraulic systems. Because of this, the system’s response time is improved and efficiency and operation accuracy are enhanced when using proportional technology instead of traditional on/off valves. Hydrofit Engineers offer its clients a wide range of hydraulic proportional valves for both industrial equipment manufacturers, as well automation integrators and high performance hydraulic systems.
What Is a Hydraulic Proportional Valve?
A hydraulic proportional valve is one that hydraulic valve is either flow, or pressure compensating and/or varying, completely proportional to an electronic signal. It utilizes a proportional solenoid to change the position of the spool, providing precise control for applications which require smooth acceleration and deceleration as well as dynamic load handling.
Proportioning valve technology is widely used in:
- Injection molding machines
- Mobile hydraulics
- Material handling equipment
- Servo-hydraulic systems
- Press machines & test benches
- Industrial automation platforms

Hydraulic Proportional Valves Features
Hydrofit’s proportional valve portfolio delivers performance-driven benefits for advanced hydraulic architectures:
- High-precision flow & pressure modulation
- Fast dynamic response with low hysteresis
- Smooth actuator movement for sensitive control requirements
- Electronic control compatibility (PWM, analog signals, controllers)
- Stable performance under variable load conditions
- Energy-efficient operation through optimized valve dynamics
These characteristics make proportional control valves indispensable in applications demanding accuracy and controllability.
Types of Hydraulic Proportional Valves
We offer a comprehensive range engineered for both flow modulation and pressure regulation.
- Proportional Flow Control Valve: Regulates flow rate proportionally to voltage/current input, ensuring smooth actuator movement.
- Proportional Pressure Control Valve: Maintains system pressure at controlled, adjustable levels based on the electrical command signal.
- Proportioning Valve: Designed for controlled pressure distribution across circuits, widely used in industrial and mobile systems.
- Proportional Solenoid Valve: Uses an electronically actuated proportional solenoid for precise spool positioning and dynamic response.
- Proportional Directional Valve: Combines directional control with proportional modulation for versatile, multifunctional control.
Proportional Valve Working Principle
A hydraulic proportional valve operates using an electromagnetic proportional solenoid that adjusts spool displacement relative to the input current or voltage. As the electrical signal varies, the spool moves proportionally, controlling:
- Flow volume
- Flow direction
- Output pressure
This enables continuous modulation rather than binary open/close movement, ensuring high-performance hydraulic actuation.
Technical Specifications
Parameter | Range / Options |
Flow Capacity | 10–250 LPM |
Pressure Rating | Up to 350 bar |
Control Signal | 0–10V, 4–20mA, PWM |
Response Time | 20–70 ms |
Mounting Style | CETOP / NG6 / NG10 / Cartridge |
Solenoid Type | Proportional Solenoid |
Medium | Hydraulic oil (Mineral/Synthetic) |
Temperature Range | -20°C to +80°C |
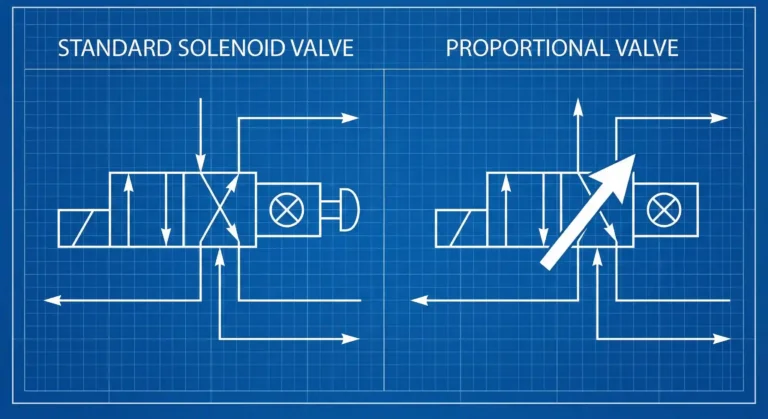
Proportional Valve Symbol:
In hydraulic circuit diagrams, the proportional valve symbol is represented using a directional valve body symbol with a diagonal arrow indicating proportional control action. This differentiates it from standard solenoid valves.
Difference Between Servo Valve and Proportional Valve
While both deliver precision control, they target different performance levels:
Aspect | Proportional Valve | Servo Valve |
Control Accuracy | High | Very High |
Response Speed | Fast | Ultra-Fast |
Contamination Tolerance | Higher | Very Low |
Cost | Moderate | High |
Application | Industrial hydraulics, mobile machinery | Aerospace, advanced test systems |
Proportional valves offer the best balance between precision, durability, and cost for mainstream industrial applications.
Hydraulic proportional valves are widely deployed in systems requiring precise and dynamic actuation:
- Plastics & injection molding machines
- Mobile machinery & construction equipment
- Servo-hydraulic presses
- Material handling equipment
- Industrial automation & robotics
- Testing and simulation systems
Their ability to deliver controllable, smooth output makes them critical in modern hydraulic motion control.
Why Choose Hydrofit Engineers?
Hydrofit Engineers offers high-performance proportional valves backed by:
- Precision engineering & repeatability
- Optimized response characteristics
- Industry-standard CETOP modularity
- Competitive India-wide supply capability
- Technical support for integration & system tuning
Our commitment is to deliver scalable hydraulic control solutions for OEMs, integrators, and industrial users. You can contact us for best proportional valve prices.
